Artificial intelligence (AI) has captured attention across nearly every industry for its seemingly boundless potential to transform how work gets done—including AI in recruiting. Yet for many talent acquisition (TA) leaders, AI remains shrouded in hype, myths and even fear that “robot recruiters” are taking over.
This handbook sets out to demystify AI tools for recruitment with facts about real-world applications across talent acquisition capabilities and provide guidance on how talent teams can start planning to use AI effectively and ethically. We’ll cut through the hype to bring AI down to earth—focusing on what works, not what’s flashy.
The message we want to reinforce upfront is that AI should not be seen as a replacement for the talent acquisition strategy you’ve already built, but rather a set of tools to make your teams better at tasks both mundane and meaningful.
📌 Before we go any further, here’s a note from our legal team:
The information provided in this article does not, and is not intended to, constitute legal or other professional advice; instead, all information, content, and materials available in this article are for general information purposes only. Readers of this article should contact their attorney or legal advisor to obtain advice with respect to any particular legal matter. No reader of this article should act or refrain from acting on the basis of information in this article without first seeking legal advice from counsel in the relevant jurisdiction. All liability with respect to actions taken or not taken based on the contents of this article are expressly disclaimed by PeopleScout, Inc.. The content in this article is provided “as-is”, and no representations are made by PeopleScout that the content is error-free.
What is AI?
The term artificial intelligence or AI was coined by Stanford Professor John McCarthy, who defined it as “the science and engineering of making intelligent machines, especially intelligent computer programs.” AI is technology with the ability to perform tasks that would otherwise require human intelligence. Data and algorithms enable AI to “learn” how to accomplish complex tasks without being explicitly programmed to do them. It also includes the sub-fields of machine learning, speech and natural language processing and robotic process automation.
Over the last decade, AI capabilities have advanced tremendously due to increases in computing power, the abundance of digital data and improvements in machine learning algorithms. As a result, AI solutions can now match or even outperform humans in certain tasks related to object recognition, language processing, prediction modelling and more.
It is critical to distinguish between two key forms: Predictive AI (Classic Machine Learning) and Generative AI (Large Language Models). Understanding this difference is the foundation of a modern AI strategy.
Predictive AI (Classic Machine Learning)
This is the traditional form of AI that has driven recruiting technology for the last decade. It uses historical data to make analysis, classification, and prediction. Its primary function is to score, filter, and identify patterns.
| Focus | Function in Recruiting | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Analysis | Scoring candidate fit based on historical success data. | Skills-based matching; Candidate ranking and scoring; Predicting early attrition risk. |
| Classification | Grouping and categorizing unstructured data. | Clustering résumés and CVs by required skills; Categorizing sentiment from employee feedback forms. |
| Prediction | Forecasting outcomes based on training data. | Predicting time-to-hire; Calculating accurate market-based salary bands. |
Generative AI (Gen AI) and Large Language Models (LLMs)
The disruption delivered by generative AI meant that AI went from an abstract concept to a tangible force radically impacting businesses—and jobs—worldwide. Instead of predicting a score, it excels at synthesis, creation, and conversation. Large Language Models (LLMs), such as ChatGPT, Google Gemini and Microsoft Copilot, are the engines of Gen AI, taking AI from expensive and exclusive to an everyday tool accessible by the masses.
| Focus | Function in Recruiting | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Synthesis | Creating coherent, human-like output from input prompts. | Drafting job descriptions and interview scripts; Summarizing interview notes; Auditing JDs for inaccessible language. |
| Conversation | Interacting with users through natural language. | Intelligent chatbots handling candidate FAQs; Creating personalized outreach based on a candidate’s public profile. |
The Future: AI Agents
The most significant development in recent years is Agentic AI. Incorporating machine learning, LLMs and predictive analytics, Agentic AI systems are designed to act autonomously to achieve specific goals, executing multi-step processes without continuous human intervention—unlike traditional pre-programmed chatbots.
Agentic AI can support:
- Recruiter support: Beyond basic automation, AI Agents act as a proactive partner for recruiters, surfacing critical insights, predicting candidate behavior and identifying emerging trends, allowing them to focus on strategic, high-value activities like relationship building and complex negotiations. It provides information needed for better decision-making through real-time analytics and predictive capabilities, while ensuring compliance and reducing potential bias.
- Dynamic personalization: Agentic AI autonomously tailors content and communications to each candidate based on their real-time browsing behavior, past interactions and career interests.
- Proactive engagement: By analyzing candidate data and behavior patterns, AI agents can anticipate needs and independently initiate relevant support or information sharing, while understanding candidate intentions and emotions.
- Question handling: Agentic AI elevates self-service capabilities by managing FAQs and knowledge bases, searching across multiple databases to resolve queries—all while continuously learning from interactions. It also audits content for accuracy and compliance while suggesting improvements to the knowledge base.
- Anticipating candidate needs: Through analysis of historical and real-time data, agentic AI predicts candidate behavior trends, helping recruiters address needs more efficiently and identify candidates at risk of dropping out. The AI agent can even independently put at-risk candidates into a re-engagement campaign.
The State of AI in Recruiting
Top talent has become increasingly scarce and competitive, while recruiting resources and budgets remain strained. This situation demands that talent acquisition teams work smarter, and AI and automation could represent an opportunity for organizations to enhance human capabilities in recruitment.
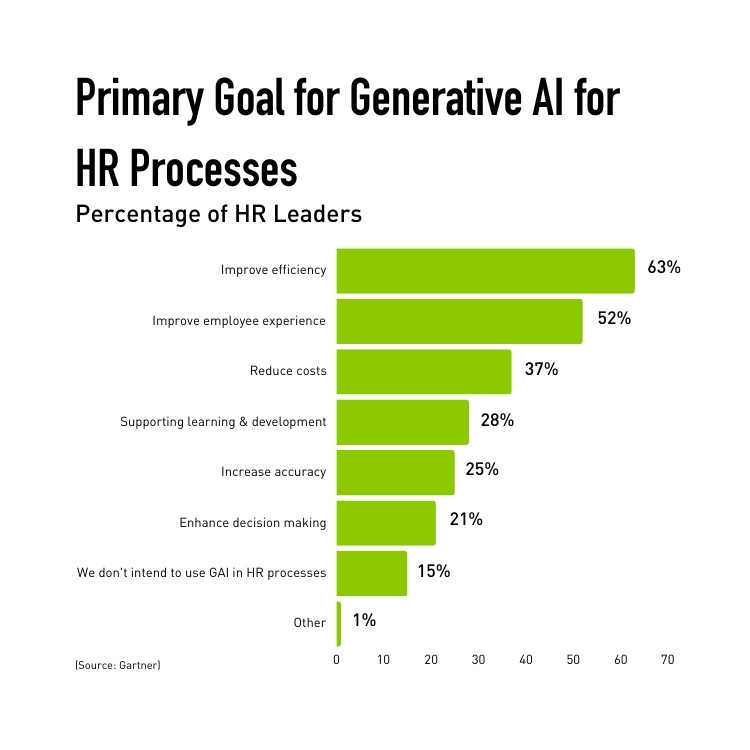
According to Gartner, a massive 81% of HR leaders have explored or implemented AI solutions to improve process efficiency within their organization. HR leaders aim to use generative AI (Gen AI) for improving efficiency in HR processes (63%), enhancing the employee experience (52%) and bolstering learning and development programs. Plus, 76% of HR leaders believe that if their organization does not adopt AI solutions in the next year or two, they will lag behind those that do.
Sign up for our Talking Talent Newsletter
Get PeopleScout’s insights sent directly to your inbox
What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of AI in Recruitment?
While AI holds tremendous promise, it also comes with some real concerns which talent acquisition and HR leaders must thoughtfully address. AI is largely unregulated and has received criticism for negative impacts on things like privacy, security, bias, and transparency in its decision-making processes. However, with care and diligence, you can establish sensible guidelines at your organization, so this technology enhances your talent acquisition capabilities while respecting human values.
Benefits of AI for Recruiting
AI can help the humans behind your talent program work more efficiently and effectively when used correctly. Applying AI across the various recruiting stages introduces a host of benefits, including:
- Efficiency
AI-powered tools can shoulder time-consuming tasks like communications and initial screening, allowing recruiters to reach more candidates at scale. AI systems help recruiters to focus their efforts on the most promising prospects, including helping identify passive candidates. This wider reach improves quality by putting recruiters in front of more qualified candidates. - Improved Candidate Experience
Tools like AI chatbots and self-scheduling create a seamless 24/7 candidate experience. By fielding frequently asked questions and coordinating interviews, they dramatically reduce time-to-hire. Candidates get quick responses instead of waiting for recruiters to come online, making the hiring process faster and frictionless. - Improved Matching
Advanced AI algorithms surface qualified prospects that may have been overlooked. By analyzing candidates’ skills, experience, and other attributes and matching them to open roles, AI systems ensure better candidate-job fit. This improves quality-of-hire and unlocks hidden talent pools recruiters may have missed. - Enhanced Diversity and Inclusion
With the right data to learn from, AI reduces unconscious bias from hiring by focusing decisions on data rather than gut instinct. By objectively evaluating candidates’ skills without prejudice, AI-assisted recruiting enhances diversity and creates a more equitable hiring process. - Cost Reduction
AI can reduce the cost-per-applicant in some cases. Recruiters can outsource low-impact, repetitive tasks to AI, and spend more time interacting with candidates and hiring managers. This optimization of talent acquisition teams enables resources to be allocated more efficiently, reducing vacancy rates and lowering costs.
Risks of AI in Recruiting
While AI offers immense efficiency, its integration introduces specific compliance, ethical, and data integrity risks that require robust organizational governance. The regulatory landscape is complex and constantly evolving, meaning organizations must adopt a proactive, audit-ready stance.
PeopleScout POV
PeopleScout is committed to striking the right balance between next-generation technology and maintaining the trust we’ve built with candidates and clients. As our clients’ trusted talent advisors, we do our due diligence and work touphold our standards for quality and compliance when helping clients adopt new technologies like GenAI.
Regulatory Landscape
The trend in global regulation is to classify AI tools used in core HR and talent acquisition as “high-risk” systems, requiring greater scrutiny. Regulations like the EU AI Act indicate a clear direction: AI systems that materially impact employment outcomes (screening, ranking, decision support) require high levels of transparency, data quality, and human oversight. Specific regional laws, such as New York City’s Local Law 144, require independent, annual bias audits of Automated Employment Decision Tools (AEDTs) and public disclosure of their usage. These localized laws set a precedent for transparency that organizations should anticipate across all operating regions.
To navigate this, organizations should consider establishing a formal AI Governance Framework:
- AI Ethics Committee: A cross-functional group (HR, Legal, Tech) responsible for approving AI use cases.
- Continuous Auditability: Mechanisms to constantly monitor models for drift and bias after deployment.
- Human-in-the-Loop: Clear protocols defining when a human expert must review and override an AI decision before final action is taken.
Hallucination
Gen AI’s ability to create plausible-sounding content can lead to a risk known as hallucination—when the model produces false, misleading or unfounded information. All AI-generated content used in external candidate communications must be subjected to a human fact-checking process before deployment.
Data Privacy and Personal Identifiable Information (PII)
The volume of data handled by recruiting AI exposes organizations to significant data privacy risks under regimes like GDPR and CCPA. Feeding Personal Identifiable Information (PII) or confidential company data into public, external LLMs poses a severe risk of data leakage and non-compliance.
To reduce this risk, organizations should adhere to strict data minimization principles, collecting and retaining data that is absolutely necessary. For training internal AI models, best practice involves anonymization techniques to scrub training data of PII and protected characteristics before it is consumed by the AI system.
Algorithmic Bias
AI models are trained on historical data, which can inherently reflect past biases in hiring practices. For example, if an AI model is trained on a dataset where, historically, male candidates were disproportionately hired for certain roles, the AI will learn to associate male-leaning language or experience with higher success, thereby reinforcing and even amplifying that bias in future decisions.
By implementing audit processes and continuous monitoring, organizations can actively measure and course-correct algorithmic bias throughout the candidate lifecycle, moving toward measurable fairness.
Disproportionate Impact
Certain demographic groups face higher exposure to the potential harms of AI in recruitment. For instance, if an AI screening system relies heavily on standardized test scores that have racial biases, it could automatically filter out qualified minority candidates. Similarly, lower income communities may lack access to the digital tools and internet connectivity required for AI screening. This digital divide could automatically exclude qualified candidates from disadvantaged backgrounds.
Without proactive measures to address these systemic issues, AI recruitment tools risk amplifying real-world inequality. Organizations must consider disproportionate impact with their use of AI in order to improve diversity and reinforce equity.
Lack of Transparency
Organizations may experience resistance amongst candidates and employees when there is a lack of understanding of how AI is being used in the hiring process and how AI arrives at certain outputs or recommendations.
You can nurture trust through training and effective communication to help recruiters, hiring managers and applicants understand the reasons behind AI-generated outcomes and their role in the hiring decision-making process. Use clear and understandable language to describe the factors influencing decisions and put mechanisms in place to capture feedback and reporting of potential issues. Transparency promotes ethical AI use in recruitment and also reinforces organizational values and establishes a positive reputation in the industry.
Data from Pew Research Center shows that 61% of Americans are unaware that employers are currently using AI in the hiring process. A majority (71%) oppose AI making a final hiring decision, while 41% oppose AI being used to review applications. However, the more people understand about AI, the more they’re in favor of its use in the recruitment process. For example, 43% of those who’ve heard a lot about using AI in the hiring process support its use for reviewing applications, compared with 37% who’ve heard a little and 21% who’ve heard nothing at all.
Over-Automation
Heavy reliance on AI also poses risks if the recruitment process becomes overly automated and fails to incorporate sound human judgment as a check. Too much automated communication can feel depersonalized to a candidate. AI should never replace the human touch—rather it should enhance human capabilities. Plus, companies using AI for recruitment must ensure compliance with all relevant regulations. For example, under GDPR, there are strict guidelines around automated decision-making, and individuals have the right to obtain human intervention and contest automated decisions that significantly affect them.
👉 Learn the dos and don’ts of automating the candidate experience.
Proactively addressing these concerns through governance, oversight and continuous improvement of AI systems and processes is key to managing the risks responsibly. Overall, the use of AI in recruitment is permitted but becoming more and more tightly regulated. Systems cannot make final hiring decisions and must be transparent, fair and accountable. Adhering to data protection laws and anti-discrimination regulations is crucial for the ethical use of AI in hiring. Undergoing regular audits to assess for unintended bias and maintaining the human touch to review, override or contest automated recommendations is crucial.
📌 We recommend you consult your legal team before implementing any AI technologies at your organization.

Use Cases for AI in Recruitment
As recruiting grows more competitive, organizations are turning to smart technologies to gain an edge in attracting and engaging candidates. From chatbots to video interviews and skills assessments, AI-powered solutions are streamlining efficiencies while enabling deeper insights across the hiring funnel. Here are some examples demonstrating AI’s immense potential to boost recruiting outcomes while improving the candidate experience.
👉 Learn how to build the ultimate recruitment tech stack.
How to Use AI for Candidate Attraction and Sourcing
Identifying, contacting and engaging prospective candidates is ripe for AI augmentation. Building a robust pipeline of talent typically involves highly manual, repetitive tasks that can divert focus away from higher-value tasks. Here are some of the ways AI can support you in filling your recruitment funnel.
Building Candidate Personas
AI can pull from the profiles of existing employees and historical hiring data for a given role to surface patterns and common characteristics. These patterns, combined with qualitative data gathered from interviews, can help you to define a persona profile of the ideal candidate for the role.
A persona is a fictional character profile that represents the different types of candidates who would be successful in a role. Personas focus on individual characteristics, behaviors, interests, goals, motivators and challenges. With these in place, you can create alignment across your recruitment and sourcing strategies. Your persona profiles should provide specific guidance about how to find candidates who fit the profile, including targeted messages that will resonate.
👉 Learn more about how to build candidate personas.
Writing Job Descriptions
Since launching in late 2022, ChatGPT and other Gen AI tools, like Claude, Gemini and more, quickly permeated the workplace. These tools mimic human communication and can help with everything from content creation and market analysis to simply writing emails. They can also be used to write job descriptions.
By feeding them with relevant prompts that detail the job tasks and required skills as well as employer brand elements like tone of voice, Gen AI can produce a first draft job description in seconds. The hiring manager and recruiter can then massage this text to create the final posting.
For existing job descriptions, AI can be used to measure sentiment and detect biased language. Recruiters can instruct Gen AI to explicitly audit an existing JD against a checklist of exclusion criteria. For instance, a prompt might include: “Review this job description and remove all hyper-masculine phrasing, ensuring the required experience is capped at five years. Output the revised text and a list of removed words.”
Job postings with gender-neutral wording get 42% more applications.
Skills Matching
AI is shifting the focus from historical job titles and degrees toward verifiable, current skills, fostering a more equitable and dynamic screening process. AI helps organizations maintain a constantly evolving skills ontology—a structured, hierarchical map of all skills required across the business.
Previously a manual process, AI can sift through a huge number of online profiles to find candidates with the skills you’re looking for. For example, the AI-powered Affinix CRM tool in PeopleScout’s total talent suite Affinix® searches millions of online profiles to find passive candidates with the skills and competencies that match the role. The AI also assesses the likelihood of a candidate being open to a new opportunity by combining the average tenure of each job listed on their profile with the average aggregate tenure of all other candidates in that same role.
Manually identifying passive candidates who have similar titles but may not be actively searching for a job can take hours of dedicated time. AI can reduce manual efforts and massively speed up the recruitment process. Plus, it helps you concentrate on skills, rather than experience, to expand your candidate pool.
Predictive Analytics
Machine learning models can also provide predictive and prescriptive hiring recommendations based on a candidate’s profile. AI can assess genuine interest, candidate motivations, likelihood to accept an offer and even risk of early turnover. This empowers recruiters to be more informed for interview prep and can help them personalize outreach messages and retention and onboarding strategies to appeal specifically to what matters most for each candidate.
Over time as engagement data is captured, AI models continue to improve, learning what messages and channels persuade candidates with various profiles and career trajectories. This creates a positive feedback loop, compounding efficiencies over each recruiting cycle.
👉 Learn more about predictive analytics in talent acquisition
Internal Mobility and Career Pathing
AI models match current employee skills and inferred career aspirations against open roles, development programs, and adjacent teams. This enables better utilization of existing talent and proactive identification of candidates for internal promotion, significantly boosting retention and reducing external recruiting costs.
How to Use AI for Candidate Screening & Interview Support
Manual candidate screening based on résumés and CVs alone can be an imperfect, biased exercise. With AI lending a “second pair of eyes,” you can ensure quality candidates are not being overlooked. Here are some elements of the process that AI can enhance.
First Sift
Natural language processing tools can ingest thousands of résumés and CVs, and analyze the content, context, and trends across the talent pool within seconds. AI maps candidate experience and skills not just against the job description keywords, but against this deeper, comprehensive skills ontology. This approach reduces reliance on potentially biased proxies (like university pedigree or irrelevant prior job titles), leading to more diverse and qualified shortlists.
Look for tools with a dashboard that highlights the “cream of the crop” candidates that demonstrate the closest alignment, enabling you to reach out or pass the most promising applicants to hiring managers quickly.
Real-Time Screening
Intelligent chatbots, like text and SMS screening tools, create a conversational experience for candidates using natural language processing. These mobile-friendly, text interview tools automatically screen candidates using predetermined questions that gauge their interest and qualifications. Based on the responses, the chatbot can instantly determine the next step for each specific candidate.
👉 Get the best practice guide for texting in recruitment.
Skills Assessments
AI is also leveraged for pre-employment assessments. New tech platforms can test and measure candidates for skills mastery, personality traits, and cognitive abilities to ensure qualified candidates are advancing through the recruitment process. All results should be reviewed by a human to ensure compliance with relevant regulations around automated decision-making. Leveraging AI in skills assessment helps ensure recruiters and hiring managers can focus on priority candidates most likely to succeed in the role, increasing equity along the way.
Want to learn more about how AI can boost your recruitment processes?
How to Use AI for Candidate Engagement
AI-powered candidate engagement tools help you create seamless, personalized experiences at scale—boosting candidate satisfaction, accelerating the hiring process and freeing up recruiters to focus on relationship building—where they add the most value.
Personalized Candidate Communications
For several years now, organizations have been leveraging candidate relationship management (CRM) technology to automate communications with candidates throughout the hiring journey. With Gen AI you can craft entire candidate communication journeys tailored to the individual’s profile, the specific stage in the funnel, and the tone of the hiring manager. Combined with automated email drip campaign functionality in the CRM, you can deliver the right information at the right stage in the journey to keep candidates informed of next steps and engaged with content that is relevant to them.
👉 Learn how to get the most out of your CRM.
More recently, recruiters are using Gen AI platforms to help them with drafting one-off emails to candidates. Leveraging the appropriate prompts, a recruiter can get a first draft from ChatGPT which they can then review and edit to fit for specific candidates. This has the potential to save hours’ worth of work each week for your talent acquisition team.
Chatbots & Conversational AI
Chatbots leverage natural language processing to manage various high-volume, repetitive inquiries from candidates. Whether answering frequently asked questions (FAQs) about application status, the interview process, the company or the job role, chatbots provide consistent, accurate responses 24/7—especially relevant when recruiters aren’t working. This improves candidate satisfaction while enabling recruiters to focus on higher-value activities.
Intelligent messaging platforms can initiate one-way communications at scale to nurture candidates. Using data on the prospect, role, process stage and more, AI dynamically generate personalized, thoughtful messages. This level of personalization improves candidate engagement, advances candidates quicker through the funnel and strengthens employment brand affinity.
Modern Conversational AI (upgraded from simple chatbots) can handle multi-modal interactions (text, voice) and take direct action in backend systems. For example, a prompt of, “Schedule an interview with Sarah for the earliest slot next week,” results in the AI checking Sarah’s and the manager’s calendars and booking the meeting directly in the ATS or calendar system.
👉 Learn more about using chatbots in recruiting.
Self-Scheduling Tools
Calendar management bots can take over the time-consuming back-and-forth of scheduling interviews, assessments, site visits and more. By integrating with hiring manager calendars, only convenient time slots are shown to candidates. Candidates automatically receive confirmations and reminders, eliminating this task for recruiters and increasing the likelihood of candidates attending interviews.

How to Get Started with AI in Recruiting
Your steps into AI should focus on exploration rather than big integrations. AI in recruitment is fast-moving and receiving more and more scrutiny from law makers, and an RPO (recruitment process outsourcing) partner can act as a strategic advisor on your AI recruiting journey. RPOs have experience implementing recruitment tech like AI software for clients and can advise on the best options for your needs, integration requirements, data needs, ethical usage, and workflow design.
By leveraging RPO expertise, companies can effectively implement AI-enhanced hiring with less disruption and a faster return on investment. Look for a partner that is moving at your speed when it comes to AI in recruiting. They’ll help you identify areas for quick wins, and help you expand this success through experimentation and testing.
Here are some ways an RPO partner can help your explore AI for recruitment:
- Change Management:
RPOs can ease the transition to automated processes and drive adoption through training and ongoing support. They can also develop training programs to upskill your in-house recruiters on using AI tools effectively and ethically in accordance with your internal AI policies. - Process Design:
RPOs can redesign recruitment workflows to integrate AI tools. For example, PeopleScout’s Talent Diagnostic examines your talent lifecycle, evaluating your employer brand and your attraction strategy, as well as looking for ways to optimize the candidate experience through technology usage. - Ongoing Optimization:
RPOs can continuously monitor and evaluate AI outputs and fine-tune processes. These insights will help you improve outcomes over time. - Compliance Monitoring:
RPOs stay current on regulations affecting AI in recruiting to advise on lawful and ethical usage in conjunction with your internal legal team.
AI in Recruiting: Potential and Responsibility
AI has demonstrated tremendous potential to transform talent acquisition. As this handbook outlines, it’s no longer just hype, rather it’s delivering real impact across sourcing, screening, interviewing and candidate engagement.
The results you’ll experience from AI depend heavily on factors like data quality, transparency, integration with existing systems and processes, and governance to ensure responsible usage. AI solutions are meant to augment—not replace—the human touch in recruitment. Recruiters are invaluable when it comes to relationship building, coaching and negotiation, and AI can’t replicate what makes them uniquely human.
Looking ahead, the use of AI recruiting technology to connect people to purpose will only continue expanding. Cultivating an ethical, inclusive and values-based recruiting culture remains key when it comes to attracting employees who align with your organization’s mission. With human stewardship over AI in recruiting, the future of talent acquisition looks bright.




