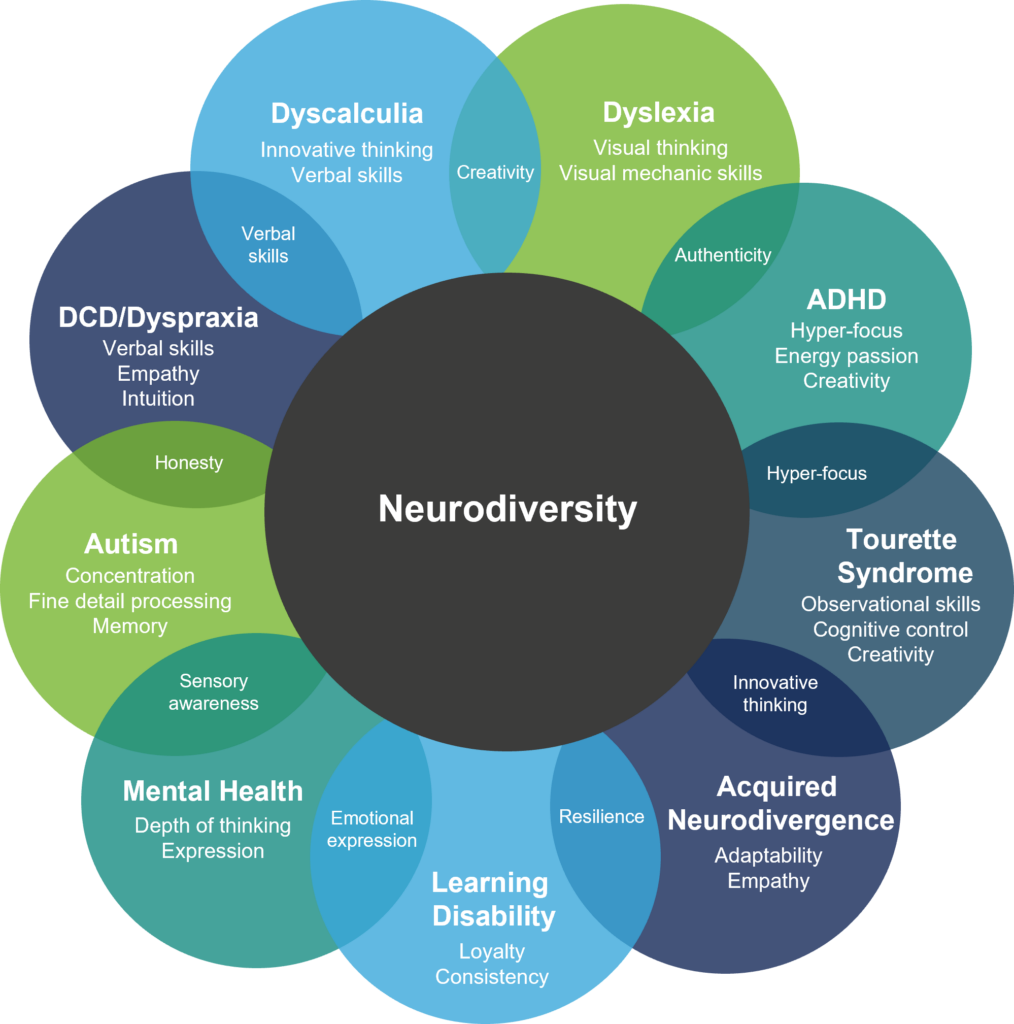
To continue our series, The Multigenerational Workforce, this article explores the challenges and opportunities of Gen Z in the workplace. For the first time in modern history, four generations are working side-by-side: Baby Boomers, Gen X, Millennials and Gen Z. The ratios will change over the coming years—and so will each group’s level of influence.
Gen Z is overtaking Baby Boomers as the largest generation history, boasting an incredible two billion people globally, and is set to become the largest demographic in the workplace by the end of the decade. Leaders must not underestimate the impact this generation’s ideas and perspective will have on the world and the workplace. By understanding their needs and preferences, you can attract, engage and hire the best Gen Z talent to propel your workforce into the future.
Who is Gen Z?
While sources vary, Gen Z is generally defined as the generation born approximately between 1995 and 2010. They are the first generation to grow up with the internet and social media and have come of age in a time marked by 9/11, polarized politics, economic fluctuations and climate woes. They watched their parents lose jobs during the Great Recession. Then, they experienced the biggest educational and workplace disruption in modern history as COVID-19 lockdowns led to their classes moving online, a surge in unemployment and psychological distress.
As voracious consumers and creators of digital media, they focus on curating their online presence and have developed an “unapologetically me” ideology. As a result, they are generally socially progressive and value diversity.
Perhaps ironically, growing up in this hyperconnected online world has also fueled feelings of isolation and loneliness among many Gen Z-ers. Seeing friends posting content and having fun (cue the #FOMO), alongside the pressure to keep on top of social trends, can make the feelings of disconnection even more acute, leading to increases in depression and anxiety.

What Matters to Gen Z in the Workplace?
Gen Z-ers have different expectations and priorities than previous generations of workers. They’ve expressed less loyalty than past cohorts and are more pragmatic. They don’t assume they’ll have a social safety net upon retirement since seeing layoffs and pensions shrinking.
Here are some more characteristics to look out for when hiring Gen Z candidates.
Fighting for Social Change
After witnessing the #MeToo and Black Lives Matter movements as well as the increased frequency of natural disasters due to climate change, Gen Z is seeking employment that matches their personal values. They believe in their ability to make a difference individually and are also demanding that employers do their part to help build a better future.
LinkedIn released a global study of nearly 10,000 professionals which found that 68% of workers in the UK, France, Germany and Ireland consider it important to work for companies that are aligned with their values. In the U.S., it’s higher at 87%. Gen Z is driving this shift, with nearly 90% in Europe saying they would leave a job to work somewhere that better matches their values.
Digitally Native but Digitally Unsure
Growing up with access to the internet and mobile devices has led to a widespread presumption that Gen Z-ers are innately good with tech. However, new research shows this may not be the case at work.
One in five of the 18-to-29-year-olds polled in HP’s Hybrid Work: Are We There Yet? report said they felt judged when experiencing technical issues in the workplace. Furthermore, this “tech shame” leads 25% of young professionals to actively avoid participating in a meeting if they think it will expose their tech shortcomings.
Generation Disenchanted?
Much has been said about the number of older workers taking early retirement, but the biggest rise in inactivity since the pandemic has not been among Baby Boomers, but workers aged between 18 and 24. In the UK, the share of workers in this age group classed as economically inactive—meaning they’re not actively working or looking for a job—stood at a record high of 32% in the second quarter of 2022. Plus, of those who are students or currently unemployed, 1 in 10 said they never intend to start working.
In a rejection of the “girlboss” and “hustle culture”, the hashtag #IDontDreamOfLabor has taken off as a platform for Gen Z to speak candidly about their rejection of work as the basis for identity, framing it instead as a financial necessity for paying the bills. In the shadow of the Great Resignation, Gen Z is vocal about the role of work in their lives—sometimes to viral acclaim. Some have taken to TikTok to coach their peers on how to negotiate salaries, which red flags to look out for in the interview process and how to stick up for what they want at work.
The formative experience of the Great Recession combined with entering the workforce during the pandemic has taught young people that hard work doesn’t necessarily guarantee stability. They want better than what their parents had and aren’t shy about demanding more from their employers. Organizations who can navigate these expectations will win the hearts of Generation Z.

Strategies for Engaging Gen Z at Work
To help Gen Z workers become as productive and successful as possible, employers need to showcase their values and offer a combination of ongoing wellbeing support and robust skills training.
1. Evaluate Your Employer Brand for Gen Z
As most young people seeking employment with a company they can believe in, it’s important to build an employer brand that resonates with Gen Z values. In the recent global study, Inside the Candidate Experience, PeopleScout found that the top things Gen Z job seekers look for when evaluating a job are:
- Mission and purpose
- Flexible working and work/life balance
- DE&I; Company culture (tied)
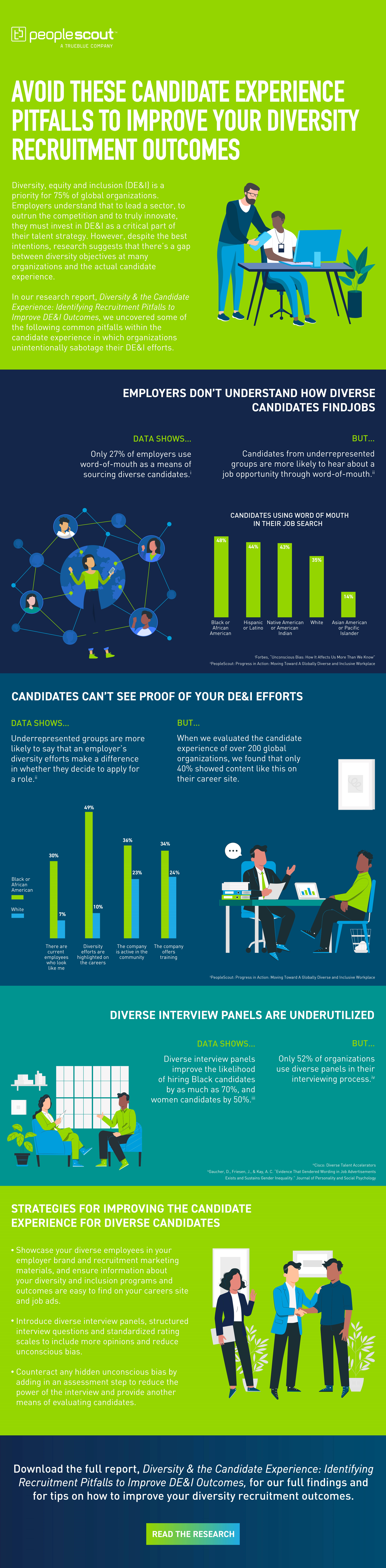
With mission and purpose as the top factor for Gen Z job seekers, it’s surprising how few organizations include this information on their career websites. On the sites we examined, we found an organization’s mission and purpose less than half (48%) of the time. This means that half of companies are passing up an opportunity to engage emotionally with their young talent audiences and assist prospects in understanding how the job they have applied for fits into that goal. Candidates won’t look at your open roles if they can’t identify your mission on your careers site.
2. Embrace Social Media
Despite concern over how much Gen Z-ers use and consume social media, it is their main way of staying connected, so it is imperative for employers to have a strong presence on social. Two-thirds of candidates use social media to research companies during their job search. Yet, a third of employers are not posting career related content (above and beyond job listings) to their social channels at least once a week.
Favorite social platforms for Gen Z include TikTok, Instagram and YouTube—so consider creating video content to engage talent from this generation. “Day in the life” videos are a great way to provide a realistic job preview and show early careers talent what it’s like to work at your organization.
3. Showcase Your DE&I Efforts
Diversity, equity and inclusion (DE&I) is a top consideration for Gen Z candidates when looking for a job, and they’ll be scrutinizing any employer to separate lip service from authentic DE&I action. When candidates from underrepresented groups are searching for jobs, the right job title might be enough to get them to click on a posting—but whether they actually apply is influenced by what they read and hear about how an organization treats its people.
Representation matters, and employers who showcase employees across a range of demographics show candidates that people from diverse backgrounds can flourish at their organization. Ensure your recruitment communications include voices and stories from underrepresented groups at all levels of the organization.
Employers should also strive for transparency with their diversity recruitment data and share any plans they have in place to shift the dial around representation. Then, when candidates from underrepresented groups encounter similar voices throughout the recruitment process, they’ll realize that not only are they welcome at the organization, but they’ll also have the opportunity to thrive and progress.
4. Offer Employee Mental Wellness Benefits
Growing up entirely in the digital age has undeniably had an impact on how this generation interacts with others. With fewer in-person exchanges, some 37% of Gen Z feels worried that technology weakens their ability to maintain strong interpersonal relationships and develop people skills. Living in a world of non-stop communication through apps and social media also contributes to mental health conditions like anxiety. The strain of modern living on mental health has been further exacerbated by the pandemic and lockdown life.
Gen Z-ers are proud advocates for mental health, sharing their experiences and removing the stigma around depression and anxiety. According to Cigna International Health’s 2023 survey of almost 12,000 workers around the world, 91% of 18-to-24-year-olds report being stressed. And they’re looking for support from their employer. A whopping 92% of university students say employers should offer mental well-being benefits, and more than a third (36%) are prioritizing those who do as they start their careers.
Employee assistance programs, employee resource groups and workplace mental health training are all ways employers are creating a culture that promotes mental health and wellbeing. Gen Z will be drawn to employers who are joining the conversation around mental health and creating a safe space to raise and address these issues.
5. Highlight Growth Opportunities for Gen Z
Worryingly, 37% of young people say their education did not adequately prepare them with the technology skills they need for their career. This digital native generation is lacking in the digital literacy most organizations need to fuel future innovation.
Gen Z is prioritizing employers who demonstrate investment in developing their employees’ skills and career paths. Employers who highlight training, mentoring and professional development programs in their recruitment materials will satisfy Gen Z’s ambition and desire to grow.
Training for new Gen Z joiners should center around soft skills like resilience, relationship building and empathy, enabling people from this cohort to manage their own stress levels effectively and to understand when and how they should ask for help. Face-to-face support and mentoring programs are a core elements of training for Gen Z in the workplace. Mentoring and reverse mentoring are being widely embraced by organizations across industries, enabling more senior employees to share their experience with the younger generation to counteract skills gaps, while also tapping into the knowledge and insights of Gen Z in the areas of social trends and digital media.
Gen Z in the Workplace: Embracing Positive Change
As organizations plan for the future of work, they must work harder to appeal to the savvy Generation Z-ers entering the workforce. While most employers understand the importance of inclusivity and ethical decision-making, this generation will hold them accountable to putting those principles into action. Employers must embrace these values and the positive changes brought by Gen Z in the workplace. Talent acquisition leaders should keep their finger on the pulse of how these young workers will shape how we hire and develop talent in the coming decades.
Check out our report to learn more about the future of work: